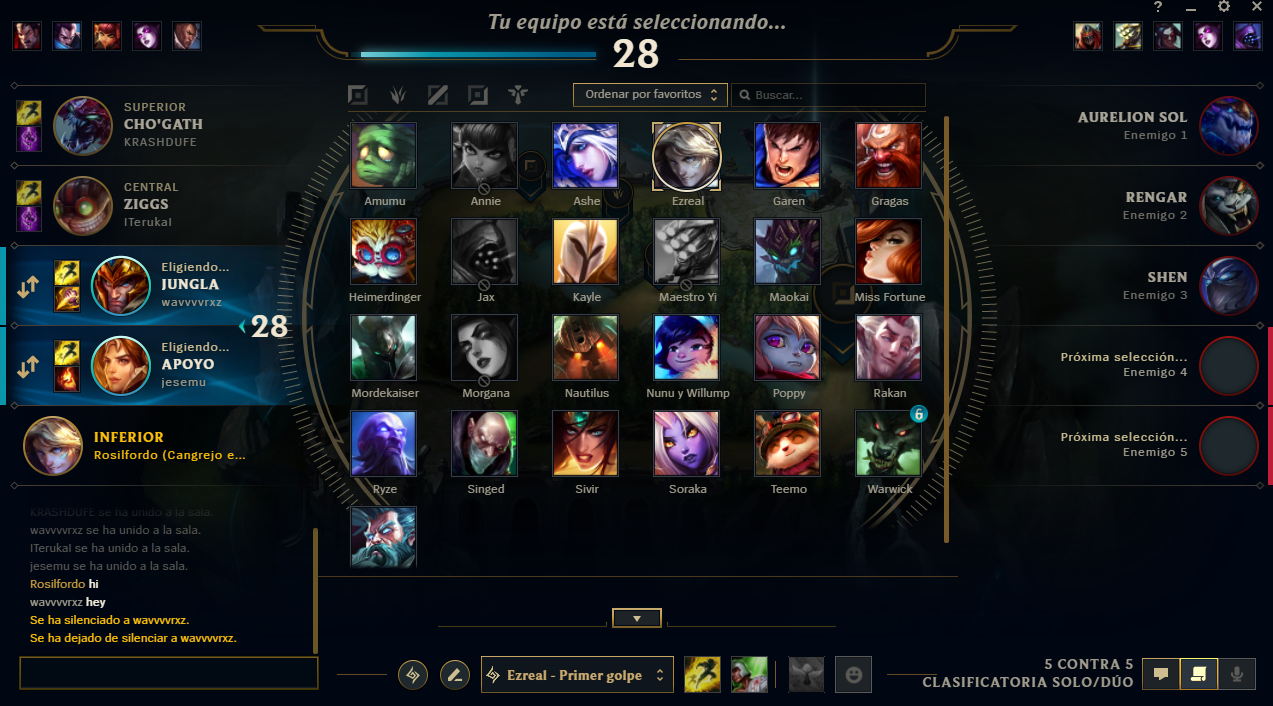
Showing names in SOLOQ champ select

This exploit was discovered by Hawolt, You can check his version here: Oldseason
Some time ago, Riot removed the possibility to see your teammates names in SOLOQ champ select. This was very useful because you could see their op.gg. But Riot started to adopt a more private policy, allowing players to hide their stats from sites like op.gg and hiding names in champ select.
After that, some people still could see their teammates names in champ select, and it was because Riot didn't actually removed the ability to see names, they just added a new flag to the RTMP messages that were sent between the client and the server saying if the player name is hidden or not.
RTMP
RTMP is a protocol used by Adobe Flash Player to communicate between a server and a client with video, audio and data. League of Legends client was built using Adobe Flash Player, then rewritten with HTML, CSS and javascript, and since then it started to migrate into a REST API model. But there are still some parts that use RTMP to communicate with the server.
How to intercept RTMP messages
To intercept RTMP messages, we need to use a proxy. If it was HTTP, we would setup a server with something like Spring, Express, Ktor, ASP.NET... and then a client with Okhttp, Axios, Fetch...
But there are almost no implementations of server side / client side RTMP (And the ones that exists, are too old or too complex). So we have to make our own using raw sockets.
RTMP Proxy
The basic structure of a RTMP proxy is:
+--------------+ +-----------------+ +--------------+
| | | | | |
| Backend | <-----> | Proxy | <-----> | LOL Client |
| | | | | |
+--------------+ +-----------------+ +--------------+First we will create the proxy, we need to know where the client is connecting to, and where we want to listen to the client.
We can get that information from the system.yaml, which is located in the league of legends installation folder.
lcds:
lcds_host: feapp.euw1.lol.pvp.net
lcds_port: 2099
login_queue_url: https://deprecated.in.favor.of.gaps.login.queue
use_tls: trueWe can change this to where we will be listening for the client
lcds:
lcds_host: localhost
lcds_port: #port that we want to listen to
login_queue_url: https://deprecated.in.favor.of.gaps.login.queue
use_tls: falseWe can also change the use_tls to false, as we are not using TLS when listening to league messages.
Now we can create the proxy server
fun LeagueProxyClient(): LeagueProxyClient {
val selectorManager = SelectorManager(Dispatchers.IO)
val socketServer = aSocket(selectorManager).tcp().bind() //This will bind to a random port
return LeagueProxyClient(socketServer, "feapp.euw1.lol.pvp.net", 2099)
}This will create a proxy with a socket server listening on a random port, and the original RTMP server feapp.euw1.lol.pvp.net and the original RTMP port 2099.
Then wait for the client to connect to the proxy
class LeagueProxyClient internal constructor(
val serverSocket: ServerSocket,
private val host: String,
private val port: Int,
) {
suspend fun start() = coroutineScope {
while (isActive) {
val socket = serverSocket.accept()
println("Accepted connection from ${socket.remoteAddress}")
launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
handle(socket)
}
}
}
...
}When the client connects to the proxy, we will handle the connection by creating a connection to the original RTMP server feapp.euw1.lol.pvp.net and the original RTMP port 2099.
The connection can use TLS perfectly (We don't want to send raw data outside of localhost)
private suspend fun handle(socket: Socket) = coroutineScope {
val selectorManager = SelectorManager(Dispatchers.IO)
val clientSocket = aSocket(selectorManager).tcp().connect(host, port).tls(Dispatchers.IO)
val serverReadChannel = socket.openReadChannel()
val serverWriteChannel = socket.openWriteChannel(autoFlush = true)
val clientReadChannel = clientSocket.openReadChannel()
val clientWriteChannel = clientSocket.openWriteChannel(autoFlush = true)
//lolServer -> proxy -> lolCLient
launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
val clientByteArray = ByteArray(1024)
while (isActive) {
val bytes = clientReadChannel.readAvailable(clientByteArray)
if (bytes == -1) {
socket.close()
clientSocket.close()
cancel("Socket closed")
}
serverWriteChannel.writeFully(clientByteArray, 0, bytes)
}
}
//lolCLient -> proxy -> lolServer
//We don't need to intercept these messages
launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
val lolClientByteArray = ByteArray(1024)
while (isActive) {
val bytes = serverReadChannel.readAvailable(lolClientByteArray)
if (bytes == -1) {
socket.close()
clientSocket.close()
cancel("Socket closed")
}
clientWriteChannel.writeFully(lolClientByteArray, 0, bytes)
}
}
}We already have a proxy that redirects the messages from the client to the server, and from the server to the client. The only thing left to do is intercept the messages that the server sends to the client and modify them.
RTMP packets structure
As said before, RTMP can be either video, audio or data. We are only interested in the data messages (The ones that are sent between the client and the server). Data comes in a format called AMF0 or AMF3, which is a format used to serialize data. It is similar to JSON, but it is not human readable.
RTMP packets are composed of a header, and a body. They are sent in chunks, and each chunk has its own header and body. When all the chunks of a packet are received, the packet is completed.
Here are some of the types used in AMF0:
- Amf0Number
- Amf0Boolean
- Amf0String
- Amf0Object
- Amf0TypedObject
- Amf0Null
- Amf0Undefined
- Amf0Reference
- Amf0ECMAArray
- Amf0StrictArray
- Amf0Date
They are similar to JSON types but more verbose.
Message Handler
We will create a class that will handle the messages that we receive from the server.
class Amf0MessagesHandler(
private val input: ByteReadChannel,
private val output: ByteWriteChannel,
private val interceptor: (List<Amf0Node>) -> List<Amf0Node> //This is the function that we will use to intercept and modify the messages
)This class will read the messages from the input channel feapp.euw1.lol.pvp.net, and write them to the output channel lol client. Intercepting the messages in between.
Chunks
To read a message, we need to read all the chunks that compose it.
private val incomingPartialRawMessages = mutableMapOf<Byte, RawRtmpPacket>()
private val completedRawMessages = MutableSharedFlow<RawRtmpPacket>()
private val outgoingPartialRawMessages = MutableSharedFlow<RawRtmpPacket>()
private val payloadBuffer = ByteArray(CHUNK_SIZE)Reading
We will read the chunks and store them in a map, until we have all the chunks that compose a message.
private suspend fun readingLoop(): Unit = coroutineScope {
while (isActive) {
val header = readHeader()
val packet = incomingPartialRawMessages.getOrPut(header.channelId) {
val length = if (header is RTMPPacketHeader0) header.length.toInt() else 0
RawRtmpPacket(header, Buffer(), length)
}
val toRead = minOf(CHUNK_SIZE, packet.length)
input.readFully(payloadBuffer, 0, toRead)
packet.payload.write(payloadBuffer, 0, toRead)
packet.length -= toRead
if (packet.length == 0) {
incomingPartialRawMessages.remove(header.channelId)
completedRawMessages.emit(packet)
}
}
}Intercepting
Now that message is completed, we can intercept it, and put it in a outgoing flow to send it again.
private suspend fun interceptingLoop(): Unit = coroutineScope {
completedRawMessages.collect { packet ->
//Only intercepting AMF0 messages
if (packet.header is RTMPPacketHeader0 && packet.header.messageTypeId.toInt() == 0x14) {
val message = AMF0Decoder(packet.payload).decodeAll().let(interceptor)
val newMessageRaw = Buffer()
Amf0Encoder(newMessageRaw).writeAll(message)
val newHeader = RTMPPacketHeader0(
chunkBasicHeader = packet.header.chunkBasicHeader,
timeStamp = packet.header.timeStamp,
length = newMessageRaw.size.toInt().toLengthArray(),
messageTypeId = packet.header.messageTypeId,
streamId = packet.header.streamId
)
outgoingPartialRawMessages.emit(RawRtmpPacket(newHeader, newMessageRaw, newMessageRaw.size.toInt()))
} else {
packet.length = packet.payload.size.toInt()
outgoingPartialRawMessages.emit(packet)
}
}
}Writing
Finally, we need to write the modified messages to the output channel in chunks (Just like they came).
private suspend fun writingLoop(): Unit = coroutineScope {
outgoingPartialRawMessages.collect {
writeHeader(it.header)
while (it.length > 0 && isActive) {
val toWrite = minOf(CHUNK_SIZE, it.length).toLong()
val asByteArray = it.payload.readByteArray(toWrite)
output.writeFully(asByteArray, 0, toWrite.toInt())
it.length -= toWrite.toInt()
if (it.length != 0) {
val firstByte =
((CHUNCK_HEADER_TYPE_3.toInt() shl 6) and 0b11000000) or (it.header.channelId.toInt() and 0b00111111)
output.writeByte(firstByte)
}
}
}
}Modifying the messages
We can modify the messages using the Amf0MessagesHandler.
private suspend fun handleSocket(socket: Socket) = coroutineScope {
val selectorManager = SelectorManager(Dispatchers.IO)
val clientSocket = aSocket(selectorManager).tcp().connect(host, port).tls(Dispatchers.IO)
val serverReadChannel = socket.openReadChannel()
val serverWriteChannel = socket.openWriteChannel(autoFlush = true)
val clientReadChannel = clientSocket.openReadChannel()
val clientWriteChannel = clientSocket.openWriteChannel(autoFlush = true)
handshake(serverReadChannel, clientWriteChannel, clientReadChannel, serverWriteChannel)
val messagesHandler = Amf0MessagesHandler(clientReadChannel, serverWriteChannel, ::unmask)
launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
messagesHandler.start()
}
//lolCLient -> proxy -> lolServer
//We don't need to intercept these messages
launch(Dispatchers.IO) {
val lolClientByteArray = ByteArray(1024)
while (isActive) {
val bytes = serverReadChannel.readAvailable(lolClientByteArray)
if (bytes == -1) {
socket.close()
clientSocket.close()
cancel("Socket closed")
}
clientWriteChannel.writeFully(lolClientByteArray, 0, bytes)
}
}
}With this, we can now see the messages that are being sent by the server.
The messages that are sent in champ select comes in a AMF0 typed object with name body.
So we will look for the body object, and check if it has a compressedPayload field (It mostly comes encoded in base64 and compressed in gzip).
After decompressing the payload, we can see that it is a json.
private fun unmask(nodes: List<Amf0Node>): List<Amf0Node> {
val body = nodes.firstOrNull { it["body"] != null }?.get("body")
val isCompressed = body?.get("compressedPayload")?.toAmf0Boolean()?.value ?: return nodes
val payloadGzip = body["payload"].toAmf0String()?.value ?: return nodes
val json = if (isCompressed) payloadGzip.base64Ungzip() else payloadGzip
...
}This is the json that we get:
{
"counter": 35,
"recoveryCounter": 0,
"phaseName": "CHAMPION_SELECT",
"queueId": 420,
"gameId": 6317386923,
"contextId": "3dd7085b-c459-4c37-a4c3-04bc7cae0ccd",
"championSelectState": {
"cells": {
"alliedTeam": [
{
"teamId": 2,
"cellId": 5,
"puuid": "549ecb51-4db6-5d74-8530-395835c9f300",
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 148987122,
"championPickIntent": 117,
"championId": 0,
"assignedPosition": "JUNGLE",
"spell1Id": 4,
"spell2Id": 11,
"skinId": 0,
"entitledFeatureType": "NONE",
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 2,
"cellId": 6,
"puuid": "92cb9260-c172-5472-995a-c81af3bcda77",
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 103187142,
"championPickIntent": 0,
"championId": 350,
"assignedPosition": "UTILITY",
"spell1Id": 3,
"spell2Id": 14,
"skinId": 350028,
"entitledFeatureType": "NONE",
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 2,
"cellId": 7,
"puuid": "d648a9eb-92d9-5a39-80ad-14a44164960a",
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 84567260,
"championPickIntent": 0,
"championId": 0,
"assignedPosition": "BOTTOM",
"spell1Id": 1,
"spell2Id": 4,
"skinId": 0,
"entitledFeatureType": "NONE",
"nameVisibilityType": "UNHIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 2,
"cellId": 8,
"puuid": "9f4bb524-9fb0-5c9e-be87-ffef73cdac8c",
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 3153038862100000,
"championPickIntent": 0,
"championId": 0,
"assignedPosition": "TOP",
"spell1Id": 12,
"spell2Id": 14,
"skinId": 0,
"entitledFeatureType": "NONE",
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 2,
"cellId": 9,
"puuid": "1b82aa86-6727-5048-bfa7-1992264f8fed",
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 83717259,
"championPickIntent": 0,
"championId": 0,
"assignedPosition": "MIDDLE",
"spell1Id": 11,
"spell2Id": 4,
"skinId": 0,
"entitledFeatureType": "NONE",
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
}
],
"enemyTeam": [
{
"teamId": 1,
"cellId": 0,
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 0,
"championId": 131,
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 1,
"cellId": 1,
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 0,
"championId": 0,
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 1,
"cellId": 2,
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 0,
"championId": 0,
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 1,
"cellId": 3,
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 0,
"championId": 0,
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
},
{
"teamId": 1,
"cellId": 4,
"summonerName": "",
"summonerId": 0,
"championId": 0,
"nameVisibilityType": "HIDDEN"
}
]
},
...
}
}You can see that the property nameVisibilityType is set to HIDDEN on allied team except for the ADC, which is set to UNHIDDEN (We are that player).
This is because we are in a SOLOQ champion select lobby.
Unmasking
Now that we understand how the champion select lobby is structured, we can start unmasking the champion select lobby.
The first thing is to check for queueId 420, which is the queueId for SOLOQ.
The second thing is to look for the property ["championSelectState"]["cells"]["alliedTeam"]
And finally iterate through every ally changing it's nameVisibilityType to VISIBLE.
private fun unmask(nodes: List<Amf0Node>): List<Amf0Node> {
...
val payload = json.deserialize().getOrElse { throw it } // Can this come in other formats?
if (payload["queueId"].asInt().getOrNull() != 420) return nodes
payload["championSelectState"]["cells"]["alliedTeam"].asArray().getOrNull()?.forEach {
if (it["nameVisibilityType"].isRight()) it["nameVisibilityType"] = "VISIBLE"
}
...
}After that, we just need to serialize the JSON back to AMF0 and send it to the client.
private fun unmask(nodes: List<Amf0Node>): List<Amf0Node> {
...
val serialized = payload.serialize()
body["payload"] = if (isCompressed) serialized.gzipBase64().toAmf0String() else serialized.toAmf0String()
return nodes
}And that's it! Now we can run the proxy, connect to it by changing the system.yaml config, and see allies names.
Some parts of the code are omitted, like the handshake, RTMP parsing, AMF0 decoding and encoding.
But the full code is available on Github, so you can check it out if you want to.